how many years does it take to study nursing
Pursuing a career in nursing is a noble and rewarding path, but the journey requires dedication and time. The duration of nursing education can vary significantly depending on the level of qualification and specialization one aims to achieve. From associate degrees to doctoral programs, the time commitment can range from two to eight years. Factors such as part-time study, prerequisites, and clinical requirements also play a crucial role in determining the length of the educational journey. Understanding these details is essential for anyone considering a future in this vital healthcare profession.
Understanding the Duration of Nursing Education
When considering a career in nursing, one of the most common questions is, how many years does it take to study nursing? The answer can vary depending on the specific degree program and the level of education you wish to achieve. Let’s delve into the details to provide a comprehensive understanding.
Factors Influencing the Duration of Nursing Studies
Several factors can influence the duration of nursing studies, including the type of degree, the educational institution, and the specific program requirements. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
Types of Nursing Degrees and Their Duration
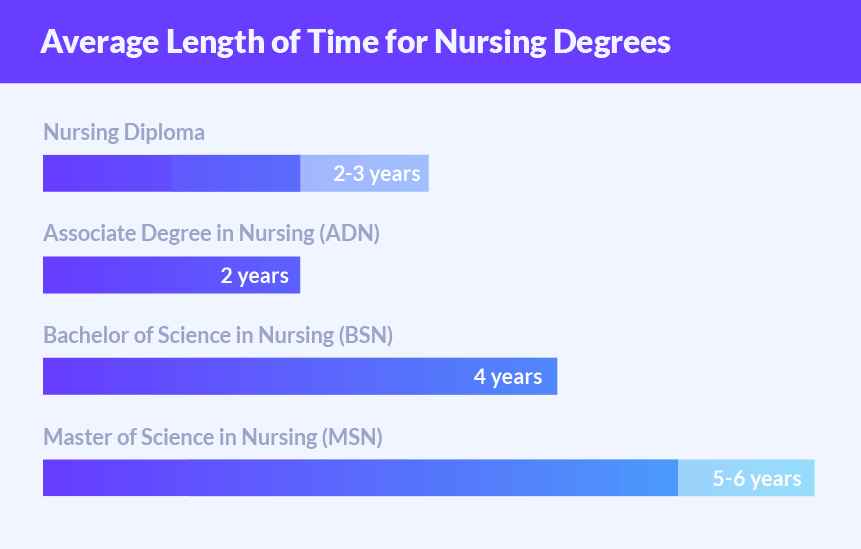
There are various types of nursing degrees, each with a different duration. Here’s a list of the most common degrees and the time it typically takes to complete them:
- Associate Degree in Nursing (ADN): 2-3 years
- Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN): 4 years
- Master of Science in Nursing (MSN): 2 years (after a BSN)
- Doctor of Nursing Practice (DNP): 3-4 years (after a BSN or MSN)
- PhD in Nursing: 3-5 years (after a BSN or MSN)
Accelerated Programs in Nursing
For those who want to expedite their education, accelerated nursing programs are available. These programs are designed for students who already have a bachelor’s degree in another field. Here are some examples:
- Accelerated BSN (ABSN): 12-18 months
- Accelerated Master’s in Nursing (MSN): 18-24 months
Part-Time and Online Nursing Programs
Many nursing programs offer part-time and online options to accommodate students with other commitments. These programs typically take longer to complete than their full-time counterparts. For example:
- Part-time ADN: 3-4 years
- Part-time BSN: 5-6 years
- Online BSN: 3-5 years
Prerequisites and Admission Requirements
Before enrolling in a nursing program, students must meet certain prerequisites and admission requirements. These can vary by institution but generally include:
- High School Diploma or GED
- Prerequisite Courses: Anatomy, Physiology, Chemistry, etc.
- Standardized Tests: TEAS, SAT, or ACT
- Letters of Recommendation
- Personal Statement
Clinical Requirements and Licensure
In addition to academic coursework, nursing programs require a significant amount of clinical experience. This hands-on training is crucial for developing the practical skills needed in the field. After completing the program, students must pass the National Council Licensure Examination (NCLEX) to become licensed nurses.
| Degree Type | Duration (Full-Time) | Duration (Part-Time/Online) |
|---|---|---|
| Associate Degree in Nursing (ADN) | 2-3 years | 3-4 years |
| Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN) | 4 years | 5-6 years |
| Master of Science in Nursing (MSN) | 2 years (after BSN) | 3-4 years |
| Doctor of Nursing Practice (DNP) | 3-4 years (after BSN/MSN) | 4-5 years |
| PhD in Nursing | 3-5 years (after BSN/MSN) | 4-6 years |
How many years of schooling does it take to be a nurse?
The number of years of schooling required to become a nurse can vary depending on the specific nursing role and the level of education you wish to achieve. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
1. LPN/LVN Programs
Becoming a Licensed Practical Nurse (LPN) or Licensed Vocational Nurse (LVN) typically requires completing a one-year program. These programs are often offered at community colleges or technical schools. The curriculum includes both classroom instruction and clinical experience. Upon completion, students must pass the National Council Licensure Examination (NCLEX-PN) to obtain their license.
- Classroom Instruction: Courses cover topics such as anatomy, physiology, pharmacology, and patient care.
- Clinical Experience: Hands-on training in a healthcare setting is a crucial part of the program.
- Licensure Exam: Passing the NCLEX-PN is mandatory to practice as an LPN/LVN.
2. ADN Programs
An Associate Degree in Nursing (ADN) program usually takes two years to complete. These programs are available at community colleges and some universities. ADN programs provide a more comprehensive education than LPN/LVN programs and prepare students to take the NCLEX-RN exam to become Registered Nurses (RNs).
- Core Courses: Students take classes in nursing fundamentals, pharmacology, and patient care techniques.
- Practical Skills: Clinical rotations in various healthcare settings are an essential part of the program.
- NCLEX-RN: Graduates must pass this exam to obtain their RN license.
3. BSN Programs
A Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN) program typically takes four years to complete. BSN programs are offered at four-year universities and provide a more extensive and in-depth education compared to ADN programs. BSN-prepared nurses often have more opportunities for advancement and specialized roles.
- Advanced Courses: In addition to core nursing courses, BSN programs include classes in leadership, research, and community health.
- Clinical Experiences: Students gain experience in a variety of healthcare settings, including hospitals, clinics, and community health centers.
- NCLEX-RN: BSN graduates must also pass the NCLEX-RN to become licensed RNs.
4. MSN Programs
A Master of Science in Nursing (MSN) program usually takes two years to complete after obtaining a BSN. MSN programs are designed for RNs who want to advance their careers and specialize in areas such as nurse practitioner, nurse anesthetist, or nurse midwife.
- Specialization: MSN programs offer various concentrations, allowing students to focus on specific areas of nursing.
- Advanced Clinical Practice: Students gain advanced clinical skills and often complete specialized clinical rotations.
- Certification: Many MSN graduates pursue additional certifications in their area of specialization.
5. PhD Programs in Nursing
A Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) in Nursing program typically takes three to five years to complete after obtaining a master’s degree. PhD programs are designed for nurses who want to conduct research, teach at the university level, or hold leadership positions in healthcare organizations.
- Research Focus: PhD programs emphasize research methods and the development of new knowledge in nursing.
- Teaching and Leadership: Graduates are prepared to teach in academic settings and take on leadership roles in healthcare.
- Dissertation: Students must complete a dissertation, which is a significant research project that contributes to the field of nursing.
What is a 2 year nursing degree called?
A 2-year nursing degree is commonly referred to as an Associate Degree in Nursing (ADN). This program is designed to provide students with the essential knowledge and skills needed to become a licensed Registered Nurse (RN). The ADN program typically includes coursework in anatomy, physiology, pharmacology, and nursing practices, along with clinical experiences in various healthcare settings. Upon completion, graduates are eligible to take the NCLES (National Council Licensure Examination) to obtain their RN license.
What is the Primary Focus of an Associate Degree in Nursing (ADN)?
The primary focus of an Associate Degree in Nursing (ADN) is to prepare students for entry-level positions as Registered Nurses (RNs). The curriculum emphasizes clinical skills, patient care, and nursing theory. Students learn how to administer medication, perform physical assessments, and provide emotional support to patients. The program also covers essential topics such as pharmacology, pathophysiology, and healthcare ethics. Additionally, students gain practical experience through clinical rotations in hospitals, clinics, and other healthcare facilities.
What Are the Admission Requirements for an ADN Program?
Admission requirements for an ADN program can vary by institution, but generally include the following:
- High School Diploma or GED: Most programs require a high school diploma or equivalent.
- Prerequisite Courses: Students may need to complete specific prerequisite courses such as biology, chemistry, and anatomy before applying.
- Entrance Examinations: Some programs may require students to take an entrance examination like the Test of Essential Academic Skills (TEAS).
- Letters of Recommendation: Some institutions may request letters of recommendation from teachers or healthcare professionals.
- Personal Statement: A personal statement or essay explaining why the student wants to pursue nursing is often required.
What Are the Career Opportunities for ADN Graduates?
Graduates of an ADN program have a wide range of career opportunities in various healthcare settings. Common roles include:
- Registered Nurse (RN): Providing direct patient care in hospitals, clinics, and long-term care facilities.
- Clinical Nurse: Specializing in specific areas such as pediatrics, geriatrics, or surgical care.
- Case Manager: Coordinating patient care and services to ensure efficient and effective treatment.
- Nursing Supervisor: Managing a team of nurses and overseeing the delivery of patient care.
- Community Health Nurse: Working in community health centers to promote public health and wellness.
What Are the Advantages of Pursuing an ADN?
Pursuing an ADN offers several advantages:
- Shorter Time to Completion: The program typically takes two years, allowing students to enter the workforce more quickly.
- Lower Cost: Compared to a four-year Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN), an ADN is often more affordable.
- Flexibility: Many programs offer flexible scheduling options, including part-time and online courses.
- Immediate Employment: Graduates can start working as RNs immediately after passing the NCLEX.
- Pathway to Advanced Degrees: ADN graduates can later pursue a BSN or higher degrees through RN-to-BSN or RN-to-MSN programs.
What Are the Disadvantages of an ADN?
While an ADN offers many benefits, there are also some disadvantages to consider:
- Limited Career Advancement: Higher-level positions often require a BSN or advanced degrees.
- Less Theoretical Knowledge: The curriculum is more focused on practical skills and may not cover as much theoretical knowledge as a BSN program.
- Competitive Job Market: In some areas, the job market for ADN graduates can be more competitive compared to those with a BSN.
- Continuing Education Requirements: To remain competitive and advance in their careers, ADN graduates may need to pursue additional education.
- Varied State Regulations: State nursing boards may have different requirements for ADN graduates, which can affect job opportunities and licensing.
Is nursing 8 years?
Is Nursing 8 Years?
No, nursing is not typically an 8-year program. The duration of nursing education can vary significantly depending on the specific degree and country. In the United States, for example, a Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN) generally takes 4 years to complete. However, there are also 2-year associate degree programs (ADN) and 1-year diploma programs offered by hospitals. Advanced degrees, such as a Master of Science in Nursing (MSN), typically add 2 additional years beyond a BSN. Doctoral programs in nursing can take 3-5 years beyond a master's degree. Therefore, the total time spent in nursing education can range from 2 to 8 years, but it is not a standard 8-year program.
Types of Nursing Degrees and Their Duration
Nursing programs vary in length and focus, catering to different career goals and educational backgrounds. Here are the primary types of nursing degrees and their typical durations:
- Associate Degree in Nursing (ADN): This is a 2-year program that provides the basic skills and knowledge needed to become a registered nurse (RN). It is often offered at community colleges and is a faster route to entering the nursing field.
- Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN): A 4-year program that offers a more comprehensive education, including leadership, research, and public health courses. BSN-prepared nurses are often preferred in many healthcare settings.
- Master of Science in Nursing (MSN): This advanced degree typically takes 2 years beyond a BSN and is required for specialized roles such as nurse practitioner, clinical nurse specialist, and nurse anesthetist.
- Doctor of Nursing Practice (DNP): A terminal degree in nursing practice that can take 3-5 years beyond a master's degree. DNPs focus on advanced clinical practice, leadership, and healthcare policy.
- Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) in Nursing: This research-focused degree can take 3-5 years beyond a master's degree and is designed for those interested in academia, research, and healthcare administration.
Factors Influencing the Length of Nursing Programs
The duration of nursing programs can be influenced by several factors, including the level of education, the specific focus of the program, and the student's prior educational background. Here are some key factors:
- Level of Degree: The type of degree, such as an ADN, BSN, MSN, or doctoral degree, significantly impacts the program length. Higher degrees generally require more time.
- Program Focus: Specialized programs, such as those focusing on nurse anesthesia or nurse midwifery, may take longer due to the additional clinical and theoretical requirements.
- Part-Time vs. Full-Time Enrollment: Students who enroll part-time will take longer to complete their programs compared to those who enroll full-time.
- Prerequisites and Prior Education: Students with prior healthcare experience or relevant degrees may be able to complete their programs more quickly by waiving certain prerequisites.
- Clinical Hours: Nursing programs require a significant number of clinical hours, which can extend the program duration, especially for advanced degrees.
Accelerated Nursing Programs
For those looking to enter the nursing field more quickly, accelerated nursing programs offer a faster route. These programs are designed for students with a bachelor's degree in another field and can significantly reduce the time needed to earn a nursing degree. Here are some details:
- Accelerated BSN Programs: These programs can be completed in 12-18 months and are designed for students with a bachelor's degree in a non-nursing field.
- Second Degree BSN Programs: Similar to accelerated BSN programs, these are tailored for individuals who already have a bachelor's degree and want to transition into nursing.
- Accelerated MSN Programs: For students with a BSN, these programs can be completed in 1-2 years and are designed to prepare advanced practice nurses quickly.
- Direct-Entry MSN Programs: These programs are for individuals with a bachelor's degree in another field who want to become advanced practice nurses. They typically take 2-3 years to complete.
- Bridge Programs: These programs, such as LPN to RN or RN to BSN, allow nurses to advance their education more quickly, often taking 1-2 years.
Continuing Education in Nursing
Nursing is a field that requires ongoing education to stay current with advancements in healthcare. Continuing education is essential for maintaining licensure and advancing in the profession. Here are some key points about continuing education in nursing:
- Licensure Renewal: Most states require registered nurses to complete a certain number of continuing education credits to renew their license, typically every 2 years.
- Certification: Many nurses pursue certifications in specialized areas, which often require additional education and passing an examination. Certifications are usually valid for 5 years and require continuing education for renewal.
- Professional Development: Nurses can participate in workshops, seminars, and online courses to enhance their skills and knowledge. These opportunities can range from a few hours to several days.
- Advanced Degrees: Pursuing a higher degree, such as an MSN or DNP, can provide advanced knowledge and open up new career opportunities. These programs typically take 2-5 years to complete.
- Research and Publications: Engaging in research and publishing articles can contribute to the nurse's professional development and enhance their expertise in specific areas.
Transitioning to Nursing from Other Fields
For individuals with a background in other fields, transitioning to nursing can be a viable career move. Here are some options and considerations for making this transition:
- Accelerated BSN Programs: As mentioned earlier, these programs are designed for individuals with a bachelor's degree in another field and can be completed in 12-18 months.
- Direct-Entry MSN Programs: These programs are tailored for individuals with a non-nursing bachelor's degree who want to become advanced practice nurses. They typically take 2-3 years to complete.
- LPN to RN Programs: For individuals who are already licensed practical nurses (LPNs), these programs can help them advance to registered nurse (RN) status and typically take 1-2 years.
- Second Career Programs: Many
How long should you study for nursing school?
How Long Should You Study for Nursing School?
The amount of time you should dedicate to studying for nursing school can vary significantly depending on several factors, including your program's intensity, your personal learning style, and your prior knowledge. Generally, nursing students should expect to study for about 2-4 hours for every hour spent in class. This means that if you have a 12-hour class week, you should plan to study between 24-48 hours per week. However, this is a general guideline, and some students may need more or less time to fully grasp the material.
Factors Influencing Study Time
The amount of time you need to study can be influenced by various factors:
- Program Intensity: Some nursing programs are more rigorous than others, requiring more study time to keep up with the pace.
- Personal Learning Style: Visual learners might benefit from diagrams and videos, while auditory learners might prefer listening to lectures or podcasts.
- Prior Knowledge: If you have a strong background in biology or healthcare, you may find some concepts easier to understand, potentially reducing the study time needed.
- Class Format: Online classes may require more self-discipline and structured study time compared to in-person classes.
- Support Systems: Having a strong support system, such as study groups or tutors, can enhance your learning efficiency and reduce the overall study time.
Time Management Tips for Nursing Students
Effective time management is crucial for success in nursing school. Here are some tips to help you manage your study time:
- Create a Schedule: Develop a study schedule that includes specific times for each subject and stick to it.
- Set Clear Goals: Break down your study sessions into manageable goals to stay motivated and focused.
- Use Active Learning Techniques: Engage in active learning methods such as practice exams, quizzes, and group discussions.
- Take Breaks: Incorporate short breaks to avoid burnout and maintain mental freshness.
- Review Regularly: Regularly review your notes and materials to reinforce your understanding and retention of information.
Importance of Self-Care
While studying is essential, it's equally important to take care of your physical and mental health. Neglecting self-care can lead to stress and burnout, which can negatively impact your academic performance. Here are some self-care practices to consider:
- Get Enough Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night to ensure you are well-rested and alert.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Maintain a healthy diet to fuel your body and brain.
- Exercise Regularly: Engage in physical activity to reduce stress and improve focus.
- Practice Mindfulness: Techniques such as meditation and deep breathing can help manage stress.
- Connect with Others: Spend time with friends and family to maintain a support network and reduce feelings of isolation.
Utilizing Resources for Success
There are numerous resources available to help you succeed in nursing school. Utilizing these resources can make your study time more effective and efficient:
- Textbooks and Study Guides: Use your textbooks and study guides as primary sources of information.
- Online Resources: Take advantage of online platforms, such as Khan Academy and YouTube, for additional explanations and practice.
- Study Groups: Form or join study groups to benefit from peer learning and support.
- Office Hours: Attend your professors' office hours to clarify doubts and gain additional insights.
- Tutoring Services: Utilize tutoring services offered by your school or seek private tutors if needed.
Questions and Answers
How long does it typically take to complete a Bachelor's Degree in Nursing?
Completing a Bachelor's Degree in Nursing (BSN) typically takes around four years for full-time students. This program provides a comprehensive education that covers both theoretical knowledge and practical skills. Students often spend the first two years taking general education courses and foundational science classes, such as anatomy, physiology, and microbiology. The remaining two years are dedicated to more specialized nursing courses and clinical practice. These hands-on experiences are crucial for developing the necessary skills to provide safe and effective patient care. Some programs may offer accelerated options for students who already have a bachelor's degree in another field, which can reduce the time to completion.
Is there a shorter program for becoming a registered nurse?
Yes, there are shorter programs available for becoming a registered nurse (RN). One common option is an Associate Degree in Nursing (ADN), which typically takes about two to three years to complete. ADN programs are often offered at community colleges and focus on the essential skills and knowledge needed to pass the National Council Licensure Examination (NCLEX-RN) and begin working as an RN. While ADN programs are shorter, they may limit career advancement opportunities compared to a BSN. However, many ADN graduates choose to pursue a BSN later through RN-to-BSN bridge programs.
What are the requirements for enrolling in a nursing program?
Enrolling in a nursing program typically requires meeting specific prerequisites and admission criteria. These can vary depending on the institution and the type of program. Common prerequisites include a high school diploma or GED, completion of certain college-level courses such as biology, chemistry, and psychology, and sometimes standardized test scores like the SAT or ACT. Additionally, many programs require applicants to have a minimum GPA, pass a background check, and complete a certain number of volunteer or work hours in a healthcare setting. Some programs may also conduct interviews or require essays as part of the application process.
Can I become a nurse in less than four years?
Yes, it is possible to become a nurse in less than four years, depending on the specific pathway you choose. As mentioned, an Associate Degree in Nursing (ADN) typically takes about two to three years to complete. Additionally, there are accelerated BSN programs designed for individuals who already have a bachelor's degree in another field. These programs can often be completed in 12 to 18 months. Another option is a diploma in nursing, which is offered by some hospitals and can take about three years. Each of these pathways has its own advantages and disadvantages, so it's important to consider your career goals and personal circumstances when choosing the right program for you.
